Top Tips for Early Childhood Educators – Where to start and what to do
Teaching Strategies for Neurodiverse Students
When working with any child with ASD it is critically important that the programme implemented is realistic, both for the child and for the family. By realistic I mean setting everyone up for (achievable) success and that everyone across all environments has the time to implement it. I believe the best way to create a realistic programme is to only address one or two ideas at any one time. I recommend in the early years you always have visuals of the goals you are working on in a prominent place (e.g. fridge or preschool office) so ALL people engaging with the child know the week’s two goals. Over the years I have found by displaying the goals ensures consistency and everyone creating opportunities to reinforce the goal. As children with autism spectrum disorders are highly individual, not all strategies may work with every child. If you find this to be the case, remember that it is worth revisiting an old strategy in the future as it may work then. Most children respond best to a range of strategies. In this podcast I have chosen two very important skills, ‘Pointing‘ and ‘Asking for Help,’ to teach children as examples of two goals you could work on at the same time.
Discussed in this Episode:
✅Focus on teaching two key skills at a time to avoid overwhelming children and caregivers
✅ Adapt teaching methods to suit the unique learning styles of children with autism
✅Create multiple visual supports for “help” and use them across all environments
✅Use co-active hand-over-hand guidance to teach pointing
✅ Use WhatsApp groups to share successes and maintain consistency across caregivers
✅Implement a choice system with preferred and non-preferred items to practice pointing
✅Introduce visuals to teach turn-taking and play skills
✅Practice fine motor skills to support the development of pointing
✅ Model asking for help in various situations throughout the day
✅Teach children to seek out specific individuals for help
✅Use pauses after communication attempts to encourage processing time
✅Incorporate help-seeking into daily routines
Perfect Early Years Teaching for Children with Autism Today!
Pointing
Pointing is a key skill to teach so children use guesture appropriately to communicate. It is a very important non-verbal means of communication. Pointing is a skill that neuro-typical often children learn spontaneously. Children with ASD usually need to be formally taught this skill, as instead of pointing they ‘drag’ or ‘lead’ adults to what they want. Even very young children with ASD can be very strong and as they grow older and stronger the adult may be injured if dragging behaviour is allowed to persist.
Pointing is a vital skill and consistency is the key.
How to Promote this Skill
- Model appropriate pointing whenever possible as you communicate with your child, e.g. when giving your child a drink, point to the drink and say “Drink” before you give it to them.
- Eye contact: in order for pointing to be an effective form of communication, the child needs to be taught to look at the other person.
- Wait. Remember to give your child time to process and then point.
-
When your child is ready to make a choice, rather than letting them grab the preferred item, anticipate their action and mould their hand gently into a point.
-
Ensure that all key adults use pointing with the child – consistency is vital in the acquisition of this skill.
-
Some children need many fine motor experiences to help them develop independent pointing. In addition to helping your child learn how to point (gently put your hand over theirs and form their index finger into a point), you may need to give your child many experiences with actions to songs and finger plays as well as a range of other fine motor activities.

Asking for Help
Learning to ask for assistance from other people is an extremely important life lesson that will benefit a child for their whole life. Once the child is able to ask for assistance when they need it, their frustration and the frequently resulting tantrums will decrease.
How to Promote this Skill
- Every time the child takes your hand to pull you somewhere, pause and clearly say “Help”.
- Once they are used to you doing this, pause longer and hopefully they will look in your direction and say “Help”. If they don’t do so, don’t get discouraged – just try again next time.
-
Once they are looking in your direction, wait a little longer and hopefully you will get eye contact, however fleeting it may be.
-
You then need to increase your expectation and expect them to vocalize any part of the word “help”.
- When the child is able to make a sound then you can then encourage them to say “help” more and more clearly.
- For children who already have single words, the adult can quickly add their name, e.g. “Help, Mummy” or “Help, Sam”.
- Use the sign for help coupled with a visual symbol as you go through the steps listed above.
If you allow your child to ‘pull you’ without prompting any language, they will continue to do this as it works.
– Excerpt from The Early Years: The Foundations for ALL Learning by Sue Larkey and Gay von Ess
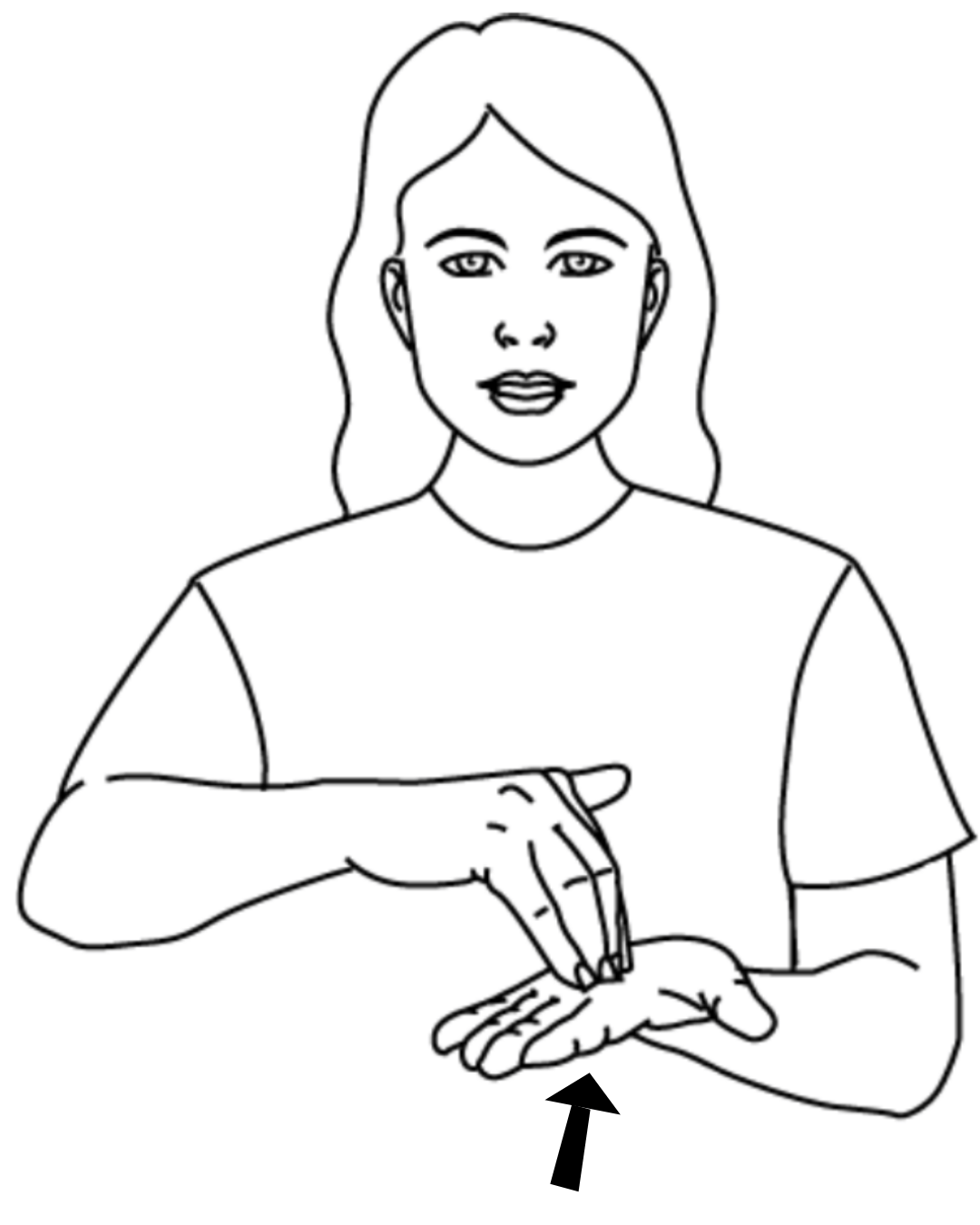
To sign help me using Auslan, form a right angle with your fingers in your dominant hand and place onto the other palm. Move towards you in a small arc.
The Early Years: The Foundations For All Learning
| by Sue Larkey & Gay von Ess | This book is full of practical ideas to give children with an ASD and other developmental delays the KEYS to learning. Teaching to play, write, draw, imitate etc. Toilet training, community access, etc. To sit, ask for help, wait, play, attention to task, sign songs, etc. Great easy to photocopy programmes.
Original price was: $39.95.$29.95Current price is: $29.95.
56 in stock
UNDERSTANDING AuDHD: Teaching & Supporting Students with Autism and ADHD Co-occurrence
✅ 2 Hours, 8 Lessons
✅ 6 Weeks to Complete 🎁 Bonus 6 Months Access (available until 28 Oct 25)
✅ Certificate of Completion
✅ Lesson Transcripts
 2 Hours
2 Hours

$149

Enjoyed learning about Early Years Teaching for kids with Autism? Try these Popular Resource for Teaching in the Early Years:
NOW IN A BUNDLE OFFER
-
Tips for Toileting
$29.95 -
Visual Learning
$39.95 -
Practical Communication Programmes
$44.95 -
Off to School Package
$340.00 -
I’m Going to School
$30.00 -
Sale!
Teach Me Art n Craft CD
Original price was: $25.00.$5.00Current price is: $5.00. -
Motivate to Communicate
$45.95 -
Songames For Sensory Processing
$49.95 -
Starting Sensory Therapy
$38.95 -
The Ultimate Guide to School and Home
$44.95






 2 Hours
2 Hours













 Sorry we no longer ship items outside Australia. Please consider the digital versions of Sue’s Books –
Sorry we no longer ship items outside Australia. Please consider the digital versions of Sue’s Books – 