For students with ASD a little extra support may be required to create friendships. For instance, when teachers allow children to select their own partners, children with ASD often are left out. Instead staff should consider who will be a good partner/ friend to the child and be pro-active in pairing them. Good examples of opportunities for schools to support friendships are in seating arrangements, partner activities and group work.
Parents, I would encourage you to support the school by organising some out of school activities such as having children over for a play, meeting in the park after school or
Joining in after school activities which friends attend. This will allow some one on one time to develop new friendships.
Why Teach This?
- Making and maintaining friendships is a constant challenge for people with ASD. Their inability to read social situations and recognise other people’s emotions can impact on their relationships.
- It is important to explore the nature of friendships with children with an ASD as they often have an egocentric view of friendship. They fail to understand that friendship is a two way thing and that it does not happen on demand.
- Children with ASD tend to be drawn to one of two more noticeable groups — either the most popular children in the class or the noisy, poorly behaved children who demand a great deal of the teacher’s attention. Children who would actually make good friends (the middle of the road group) tend not to be noticed by the child with ASD.
- Children with Asperger’s Syndrome in particular want friends but frequently burn these friends out by their inappropriate expectations of friendship. Parents and teachers have to reinforce and acknowledge these friends to help keep the friendships going. Having a number of friends, possibly a couple allocated to each day of the week can help alleviate the demands on the mainstream friends.
Ideas for Teaching at School and Home
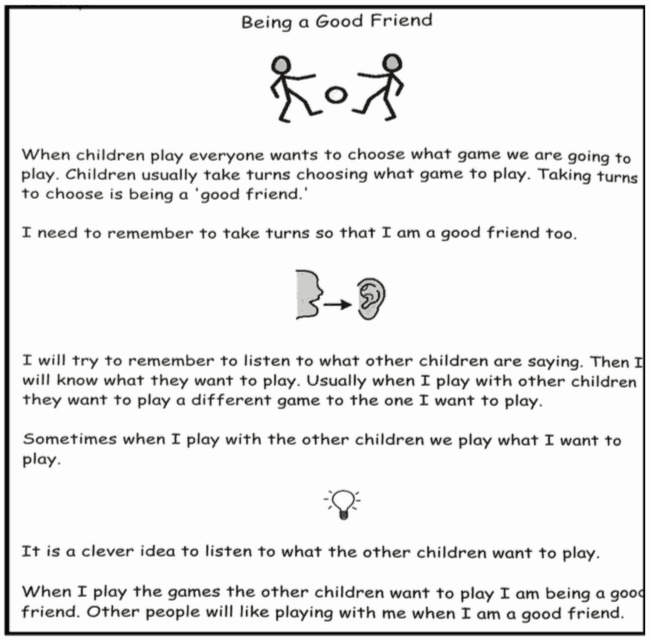
- Discussions on what a friend and what friendship really are -emphasise that friendship is a two way thing.
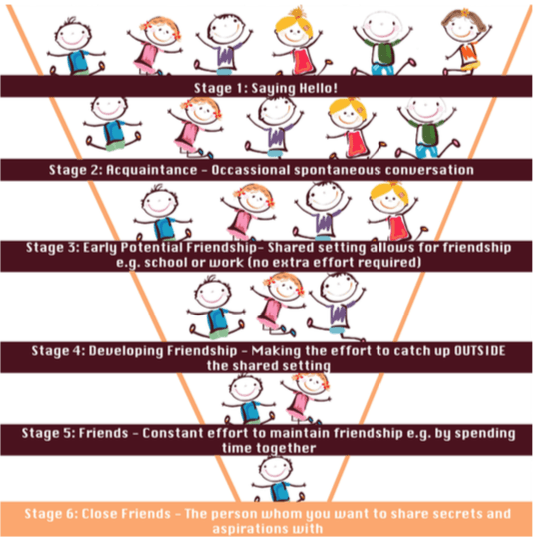
- Use the Friendship Funnel below to explain the stages of friendship. Discuss as a whole class or as a family who would fit in those different stages of friendship. Download the visual here
- Foster friendships by establishing buddy systems for primary school age children and mentors for older children with ASD. It is important that several buddies/mentors be allocated to each child with ASD to ensure that the other children do not find this too much of a responsibility.
- Run supervised clubs for the whole school at break times, especially long lunch-times. A variety of indoor and outdoor activities could be offered e.g. Lego, chess or computers. Often all children, not just those with ASD,will benefit from extra activities. Involve older students, parents, grandparents and other interested people in the community if at all possible.
- Discuss and brainstorm friends and friendships. Aspects could include:
- Like to play together
- Share
- Let other people be first sometime
- Take turns
- Listen to other people’s ideas
- Let other people choose WHAT to play sometimes
- Like the same things
- Have the same sense of humour
- Like to talk together
- When students need to break into pairs or small groups; teachers can encourage inclusion by asking students to pair up/group by eye colour or letters in their name etcExcerpt from Developing Social Skills by Sue Larkey and Gay von Ess. Click here for more information about the book.
Don’t miss out on any Sue Larkey content!
Subscribe at the bottom of the page


 Sorry we no longer ship items outside Australia. Please consider the digital versions of Sue’s Books –
Sorry we no longer ship items outside Australia. Please consider the digital versions of Sue’s Books – 